There are three feasible wideband channel measuring methodologies in the THz band:
(1) frequency-domain channel measurement based on VNA;
(2) time-domain channel measurement based on sliding correlation;
(3) time-domain channel measurement based on THz-TDS.
VNA-based Channel Sounder
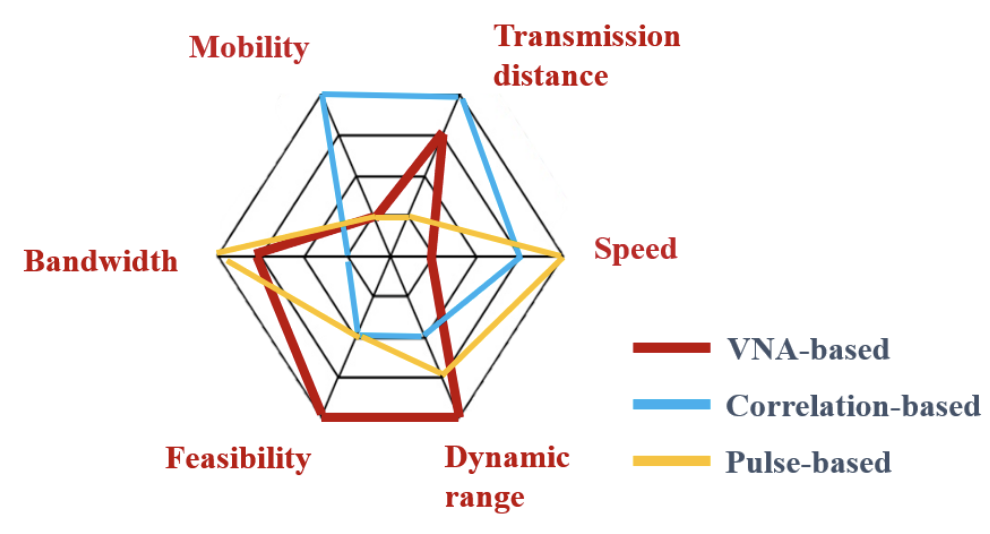
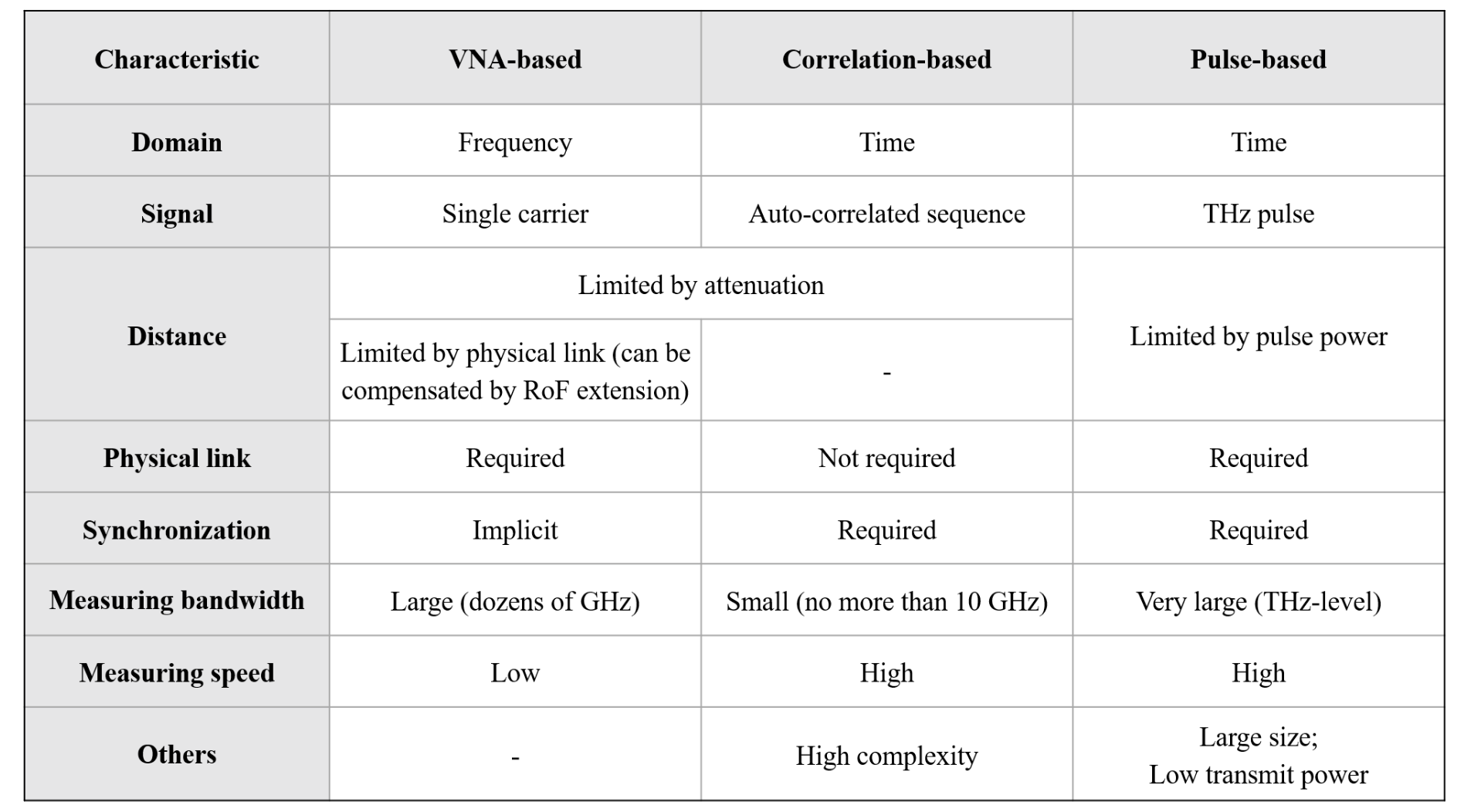
The channel measurement platform supports the frequency ranging from 260 GHz to 400 GHz. The system is composed of the Tx module, the Rx module, and the Ceyear 3672C VNA. The VNA generates radio frequency (RF) and local oscillator (LO) sources. The signals from RF and LO sources are multiplied by 27 and 24, respectively. As a result, the transmitted signal reaches the carrier frequencies ranging from 260 GHz to 400 GHz, and the mixed intermediate frequency (IF) signal has the frequency of 7.6 MHz. The IF signals at Tx and Rx modules are both sent back to the VNA, and the transfer function of the channel is calculated as the ratio of the two frequency responses.
* We appreciate the collaboration with Ceyear, Nanjing Nuo Zhi Jie and National Instruments to establish our channel measurement system.
Correlation-based Channel Sounder
The correlation-based channel sounder consists of a transmitter (Tx) and a receiver (Rx). At both Tx and Rx, there are a chassis for baseband processing, and a radio frequency (RF) front end for RF transmission/reception. Moreover, rubidium (Rb) clocks are utilized to provide clock reference and 1 pulse-per-second (1PPS) trigger to the local oscillation (LO) sources and chassis. Before conducting channel measurements, two Rb clocks at Tx and Rx are connected in a master-slave mode for several hours to synchronize the 1PPS signal. Mechanically, the up/down converters are installed on rotators, lifters, and carts, to conveniently change their steering directions, heights, and positions, respectively.
Different from the VNA-based channel sounder, no cable connection is needed using the correlation-based sounder, for which it is convenient to conduct long-distance outdoor channel measurements. Specifically, through a 5000-times average, the noise floor is lower than 160 dB, for which the measurable distance with a 30 dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the line-of-sight (LoS) case exceeds 200 m. As another advantage especially useful in dynamic scenarios, the measurement speed is fast, tak ingaround 6 ms to record one channel impulse response (CIR).
THz-TDS System
The THz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) system covers a broad frequency range from 0 to 6 THz and employs ultrafast electromagnetic pulses in the THz spectrum to probe material samples, making it suitable for characterizing both the reflection and transmission properties of a wide variety of materials. A femtosecond laser pulse generates a broadband THz pulse, which interacts with the material under test. The transmitted THz pulse is then detected by a photoconductive antenna, providing time-domain data for further analysis. The sample under test is positioned at a fixed 9 cm from the antennas, with an incidence angle of 10 degrees.